Extended Fraud Reasons
General Information¶
FraudScore evaluates traffic based on over 150 parameters. All parameters are grouped into 34 categories. In some categories, analysis may be performed simultaneously by multiple algorithms detecting different anomalies.
These categories are called Extended Fraud Reasons - more detailed (extended) reasons for fraud.
There is a higher-level division into Fraud Reasons. However, the analysis primarily uses Extended Fraud Reasons, which are listed below.
- os - suspicious distribution of devices in traffic (device models, browser versions, operating system, etc.).
- duplicate IP - multiple conversions from the same IP or IP subnet.
- duplicate device - multiple conversions from the same or very similar device.
- ip distribution - anomalous distribution of IP addresses detected.
- emulator - device emulator (e.g., Bluestacks).
- fake device - fake device parameters and their combinations - identifiers (user agent, IDFA/Android ID, MAC address, etc.).
- clickspam - an app installation attributed to a click, which is an organic installation captured by an ad network through user fingerprint spam algorithms.
- refer host - a click made from a suspicious website.
- low tti - the anomalously low time between click and conversion; in the case of Android conversions, a sign of click injection.
- flat tti - anomalous distribution of time between click and conversion, a sign of click-spamming.
- overall flat tti - an essential parameter for detecting TTI deviations. This parameter processes traffic through broader slices and can be used in conjunction with "Flat TTI" or independently.
- low variance tti - when the TTI parameter raises suspicion due to low variance in the actual installation time for many conversions.
- tor - the IP is an exit point of the TOR network.
- datacenter - traffic coming from servers in data centers or known cloud platform providers, rather than residential or corporate networks (very low likelihood of a real human user).
- geo mismatch - evidence of user location spoofing.
- proxy context - a considerable large number of IPs in the current segment are flagged with the
proxyreason. - dynamic proxy - denotes dynamic IPs of mobile operators acting as proxies, which may not be directly related to fraud.
- proxy - for IP addresses acting as proxies but not directly linked to fraud.
- duplicate proxy - multiple conversions from addresses that were flagged with the
proxyreason. - blacklist - IP addresses recently connected to a device involved in fraudulent activities, potentially vulnerable, or showing suspicious activity.
- dynamic blacklist - for IPs associated with fraud activity similar to Blacklist, but flags conversions made from mobile operator IPs.
- old browser version - an outdated web browser version is used. The version should be more recent and up-to-date.
- outdated browser version - a very outdated web browser version.
- crawler - a symptom indicating the use of a crawler application (e.g., a search engine).
- duplicate build - a large number of conversions coming from the same Android build version.
- regional specific device - anomalous location of a device released for a specific region (market).
- no events - a large proportion of conversions lack in-app activity.
- ISP anomaly - a predominant number of conversions from a single ISP.
- bad events - suspicious in-app activity, anomalous metrics in most events.
- lowcr - anomalously low conversion rate from click to installation, typically a sign of click-spamming.
- highcr - a symptom indicating an anomalously high conversion rate from click to conversion (installation or registration). This characteristic is typical for sources with bot-driven devices and may indicate the presence of incentivized users.
- multiple attribution - multiple conversions with anomalous distribution of attribution parameters.
- CTR anomaly - anomalous rate of transitions from impressions to clicks in the impression-click-install funnel, typically a sign of click-spamming in attribution based on both impressions and clicks.
- obsolete system params abuse - a vulnerability where attackers deliberately use outdated system or device configuration parameters.
Each detected reason assigns a fraud score (Fraudscore) to the conversion, ranging from 1 to 100 points depending on the severity of the violation. If multiple anomalies are detected for a conversion, the fraud scores are summed. Based on the total fraud score, the conversion falls into a specific risk zone (ok, low, mid, high).
Tip
The scoring system (Fraudscore) is applied not only to conversions but also across various dimensions, such as Offer, Affiliate, etc. This allows you to view the average risk score for an Offer, Affiliate, etc. In such evaluations, we recommend paying attention to the average score for a dimension starting from 25 Fraudscore.
Tip
As a general rule, we recommend rejecting only 

Grouping¶
FraudScore offers a unique opportunity for a deeper understanding of the reasons for detecting fraud in analyzed traffic. This is achieved through groupings by Fraud Reasons and Extended Fraud Reasons.
Enable grouping by Fraud Reasons to view high-level fraud categories.
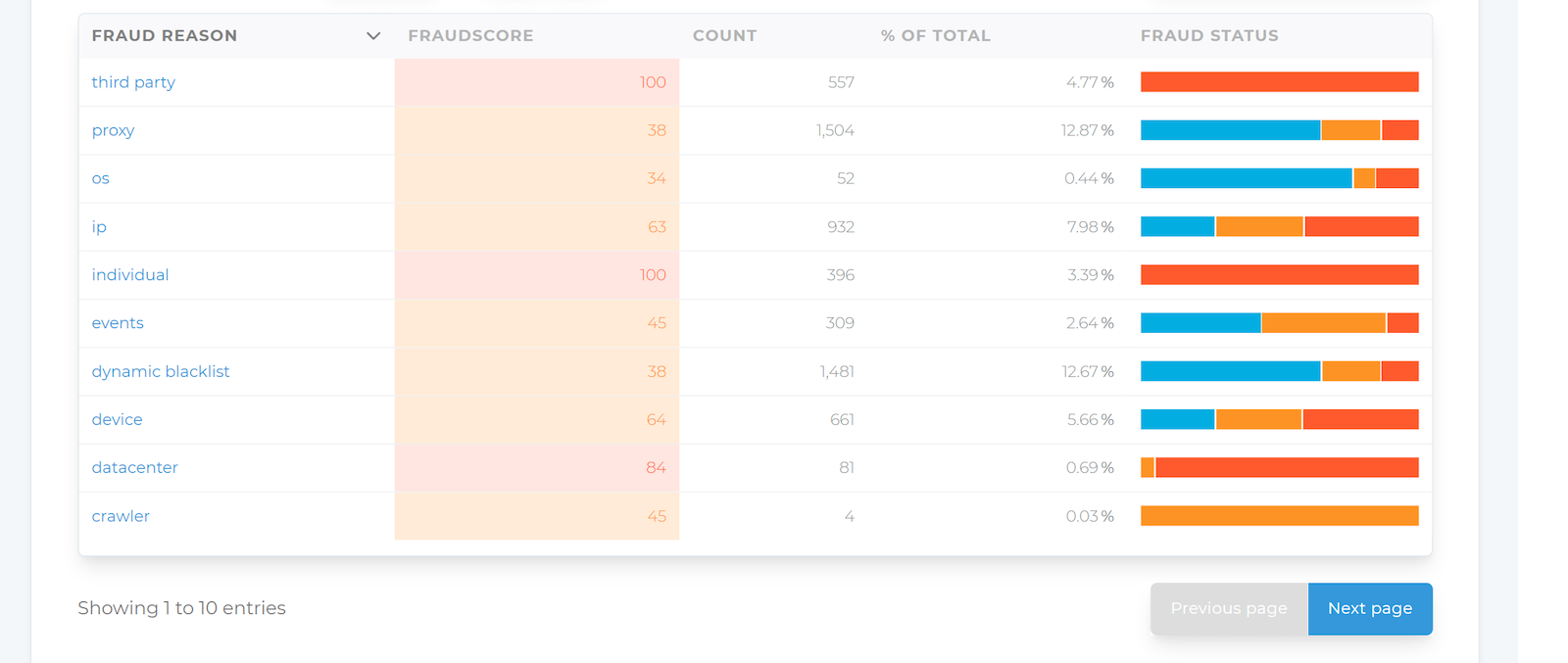
Alternatively, activate grouping by Extended Fraud Reasons to see more detailed reasons.
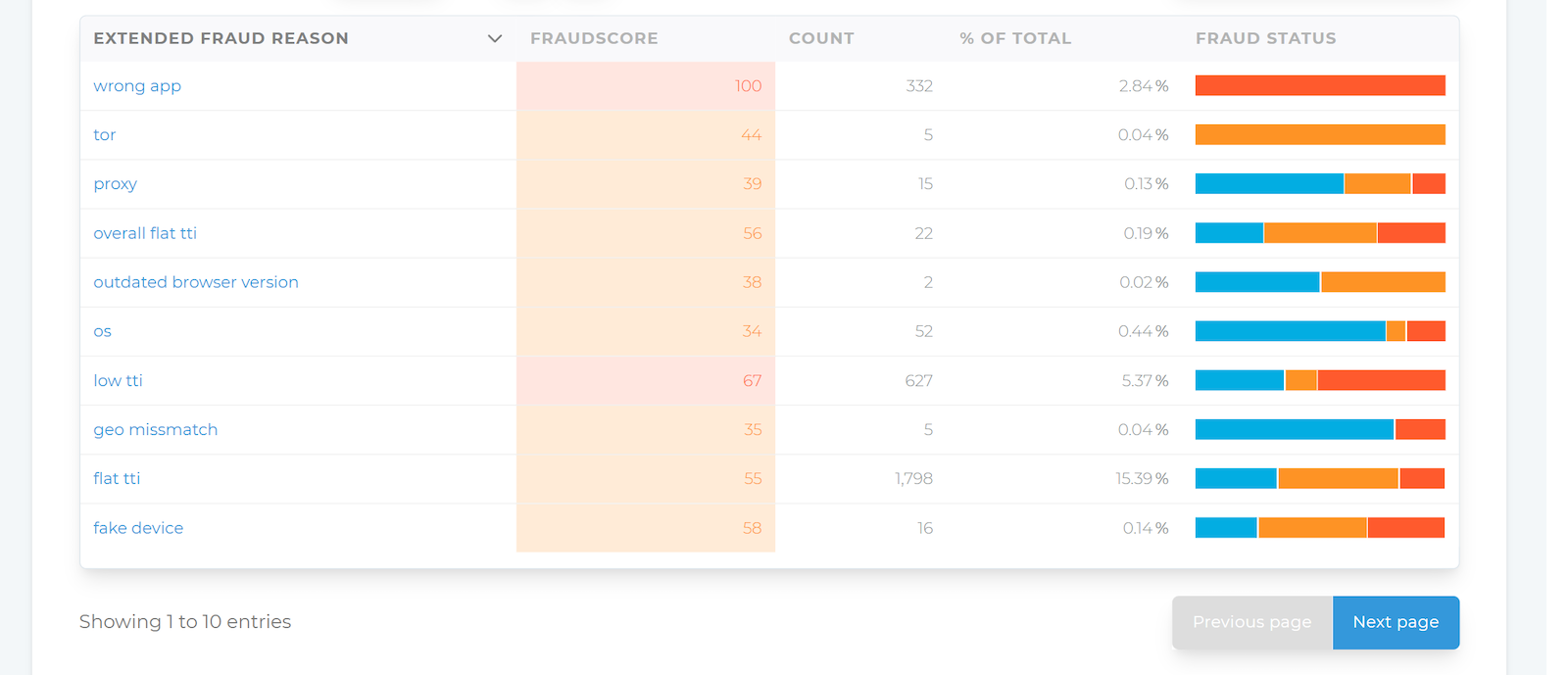
Groupings can be combined with each other and with other parameters. For example, group by Offers and Extended Fraud Reasons to assess the reasons for fraud for a specific Offer.
Information
A single conversion can be flagged with multiple reasons and, accordingly, when grouped by Fraud Reasons or Extended Fraud Reasons, it will appear in multiple groups.